Life insurance is a payment contingent upon the death of an insured life.
General formula
The present value at age 𝑥 of a life insurance with a payment of 1, paid at the end of the year of death is calculated by this formula:
![]()
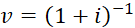
Types of life insurances
To get detailed information about a specific type of life insurance, click its name in the first column.
|
Type
of Annuity |
Description |
|
Life insurance |
A payment contingent upon the death of an insured life. |
|
A payment contingent upon the first death of two insured lives. |
|
|
An insurance which provides a payment only if death
occurs within a limited number of years |
|
|
An insurance which provides a payment only if death
occurs after a number of years. |
|
|
An insurance which provides a death benefit that
increases by 1 with each passing year. |
|
|
An insurance which provides a death benefit that increases by 1 with each passing year, with no death benefit paid if death does not occur within a limited number of years. |
|
|
A decreasing life insurance provides an initial death
benefit of 𝑛 decreasing by 1 with each
passing year. If death occurs after 𝑛 years then no
payment is made. |
A payment contingent upon the death of an insured life.
The present value at age 𝑥 of a life insurance with a payment of 1, paid at the end of the year of death is calculated by this formula:
![]()
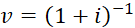
where
· the interest discount is
![]()
· ![]() probability that (𝑥) will survive to age 𝑥 + 𝑡 and die within 1 year
probability that (𝑥) will survive to age 𝑥 + 𝑡 and die within 1 year
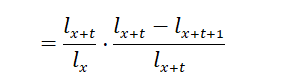
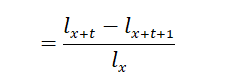
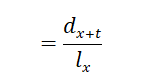
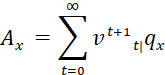
·
![]() the
number of lives surviving to age 𝑥 in a population of
the
number of lives surviving to age 𝑥 in a population of ![]() lives at age 0
lives at age 0
·
![]() the
number of lives at age 𝑥 who die before the attainment of age 𝑥 + 1
the
number of lives at age 𝑥 who die before the attainment of age 𝑥 + 1
For simplicity, the upper limit of the summation is infinity because the probability of survival becomes zero at age 𝜔 (omega), the terminal age in mortality table.
Using commutation functions, the present value formula of life insurance is:
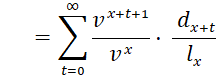
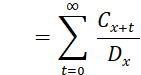
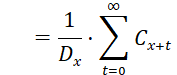
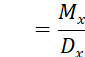
![]()
If the payment is made prior to the end of the year, adjustments
are made based on certain simplifying assumptions.
A payment contingent upon the first death of two insured lives 𝑥 and 𝑦.
The present value at joint age (𝑥𝑦) of a joint life insurance with a payment of 1, paid at the end of the year of the first death of either 𝑥 or 𝑦 is calculated by this formula:
![]()
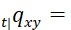
where
· the interest discount is
![]()
· ![]() probability that both 𝑥 and 𝑦 survive 𝑡 years to ages 𝑥 + 𝑡: 𝑦 + 𝑡, and one or both die within 1 year after that:
probability that both 𝑥 and 𝑦 survive 𝑡 years to ages 𝑥 + 𝑡: 𝑦 + 𝑡, and one or both die within 1 year after that:
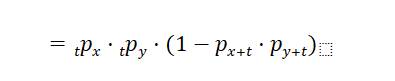
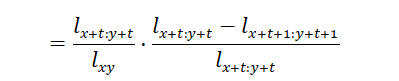
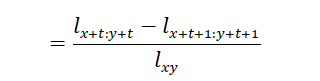
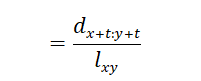
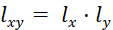
·
![]()
·
![]()
For simplicity, the upper limit of the summation is infinity because the probability of survival becomes zero at age 𝜔 (omega), the terminal age in mortality table.
Using commutation functions, the present value formula of life insurance is:
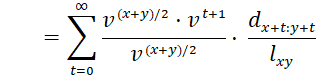
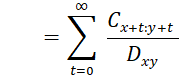
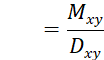
![]()
where
![]()
![]()
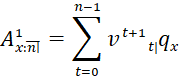
Term insurance (temporary life
insurance)
An insurance which provides a payment only if death occurs within a limited number of years.
The present value at age 𝑥 of an n-year term insurance is calculated by the formula:
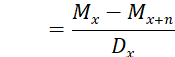
![]()
An insurance which provides a payment only if death occurs after a number of years.
The present value at age 𝑥 of an n-year deferred insurance is calculated by the formula:
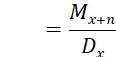
![]()
An increasing life insurance provides a death benefit that increases by 1 with each passing year.
The present value at age 𝑥 of an increasing insurance is calculated by the formula:
![]()
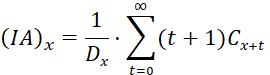
Using commutation functions, the present value formula of an increasing life insurance is:
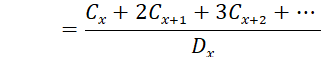
![]()
![]()
![]()
An increasing term insurance provides a death benefit that increases by 1 with each passing year, with no death benefit paid if death does not occur within a limited number of years.
The present value at age 𝑥 of an increasing term insurance is calculated by the formula:
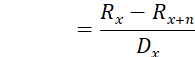
![]()
A decreasing life insurance provides an initial death benefit of 𝑛 decreasing by 1 with each passing year. If death occurs after 𝑛 years then no payment is made.
The present value at age 𝑥 of a decreasing insurance is calculated by the formula:
![]()
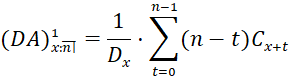
Using commutation functions, the present value formula of a decreasing life insurance is:
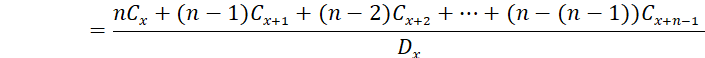
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Excel functions
Click here
to see the various Excel functions to handle life insurance.